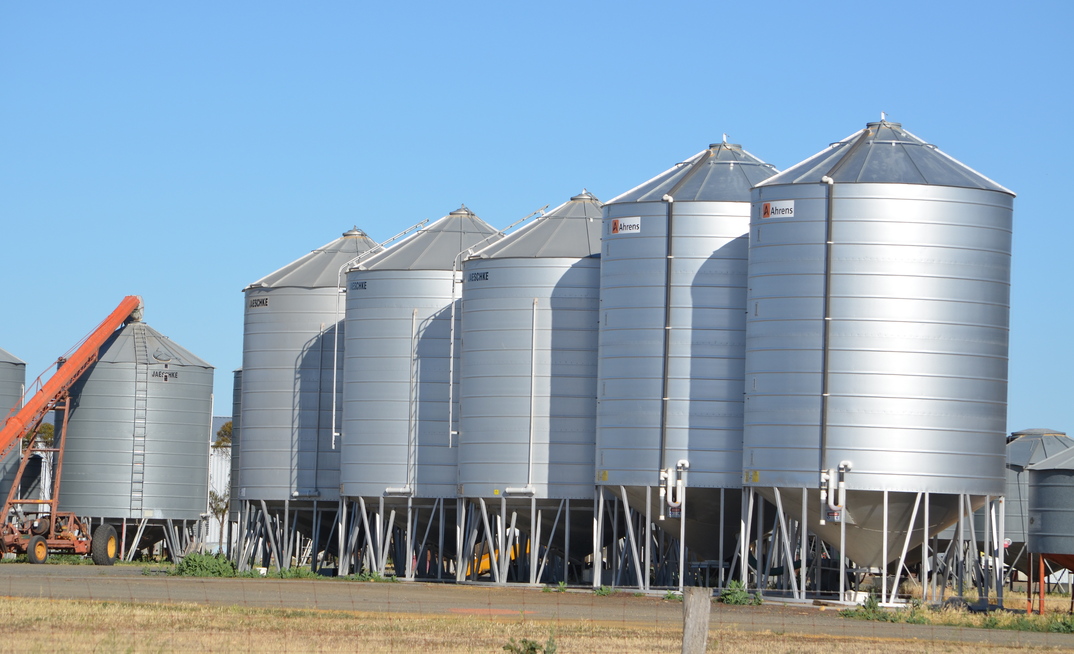
WHEAT falling number test results could improve with time in storage, according to new preliminary research findings, which support what Australian growers have been reporting anecdotally.
The findings are part of a new research investment by the Grain Research and Development Corporation (GRDC) and Agriculture Victoria, supported by New South Wales Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development (NSW DPIRD) and LongReach Plant Breeders.
GRDC grain storage extension team lead, Chris Warrick, said trials by Agriculture Victoria's research team at Horsham SmartFarm indicate wheat falling number could increase by up to 50 seconds and even exceed 300 seconds post storage. However, he said barley shows no increase, and further research is needed to understand the differences.
While Warrick said the preliminary results were encouraging, he added further research is needed to test the results across more varieties to better understand how growing and storage conditions might influence a change in falling number.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
SURPASSING WHEAT FALLING NUMBER THRESHOLD
The preliminary research found wheat with an initial falling number test result over 250 seconds has the potential to increase and surpass the 300-second threshold required for various Australian wheat grades during storage. It showed increasing the falling number by 40-50 seconds took 4-6 months.
While cold storage is best for mould and insect prevention, the research indicates storing wheat at 25-30 degrees Celsius may boost the likelihood of increasing the falling number test results compared to colder temperatures.
The wheat used in the research had a moisture content of 11 per cent and was stored at 45 per cent humidity, but researchers said the impact of varying moisture levels on falling number changes is still unknown.
Agriculture Victoria research leader, Dr Cassandra Walker, said where wheat had an initial falling number of less than 250 seconds, no change in falling number was observed.
"We are not talking about magic, specific storage conditions are essentially an attempt to stop the very early stages of germination," she said.
RESEARCH NOT YET REPLICATED ON-FARM
Warrick said the research has yet to be replicated in farm storage conditions.
"We are sharing these early results to give growers the opportunity to decide if they want to try storing wheat that doesn't quite make the 300 second falling number test and see if it improves with storage," Warrick said.
We certainly don't want to create an expectation that these results will be replicated in all conditions, there are still many variables and influences we need to understand through further research."
Warrick reminded growers that aside from falling number considerations with storage it is also critical they prioritised safe grain storage practices, including regular monitoring of grain temperature and moisture, and using a sieve and probe traps to detect insects.
"It would be counterproductive if we chase an increase in falling number at the expense of letting grain go mouldy or become damaged from insect pests such as weevils," he said.
"We aim to cool grain immediately after harvest to maintain seed viability, preserve grain colour, prevent mould, and deter insects."
Warrick said, in theory, operating aeration cooling fans as usual for the initial phases as soon as the storage was full then reducing fan runtime once grain temperature was in the 25-30 degree Celsius range, to delay further cooling for grain moderately low in falling number, could have positive outcomes for the falling number test result.
"As soon as the target falling number result is reached, if it's reached, then aeration cooling would be continued to provide safer storage conditions, reducing the chance of spoilage from mould or insects," he said.
POTENTIAL TO BOOST WHEAT PRICE BY $150/T
Warrick said the research could have significant benefits for Australian growers if well managed storage can help wheat reach the next grade to return an extra $50-$150 per tonne.
"GRDC's proactive approach in recognising the opportunity to conduct preliminary research when conditions presented at short notice could prove a major game changer for growers," he said.
"This research would not have been possible without the prompt cooperation and investment from GRDC and the support from the Agriculture Victoria Research Horsham SmartFarm team and NSW DPIRD field trials team, along with LongReach Plant Breeders who provided samples."
For more information on managing grain in storage, download a copy of the GRDC Grain Storage GrowNotes from storedgrain.com.au or call your nearest grain storage specialist on 1800 WEEVIL (1800 933 845).